PMA - Going even further: Lab07-02

The downloader alien
Introduction
Hello there, In this blog, we’re going to reverse engineer another lab from the Practical Malware Analysis book!
Obs: This malware’s code (Lab07-02.exe) is present in two other labs (Lab01-03.exe & Lab18-02.exe), which are the same binary. The only difference is that those labs use a packer. So, in the end, the final code is Lab07-02. So, let’s dive in!
Triage fase:
Nowadays, I hardly spend much time doing triage. Normally, I run in a sandbox and wait for the results. The only things that I keep an eye on are:
- Imported functions (or exported when DLLs);
- Strings;
- PE sections, overlays, entropy (for packing indications);
After that, I just run CAPA against the binary to get an idea of its capabilities.
Pestudio shows us an indicator of a URL (hxxp://www[.malwareanalysisbook.]com/ad.html). This indicates that this may be a downloader.

Suspicious URL
The relevant functions used by this binary are:
- ole32.dll:
- OleInitialize
- OleUninitialize
- combase.dll:
- CoCreateInstance
- oleaut32.dll:
- SysAllocString
- SysFreeString
As we can see, this program uses COM (Component Object Model) to interact with the system. For those who don’t know about COM, it is basically an interface that makes it possible for different software components to call each other’s code without knowledge of specifics about each other.
A good resource to learn about COM is, of course, the Microsoft documentation, but if you don’t want to read the full doc, this post may help you get a feeling about this topic.
The results from CAPA are the following:
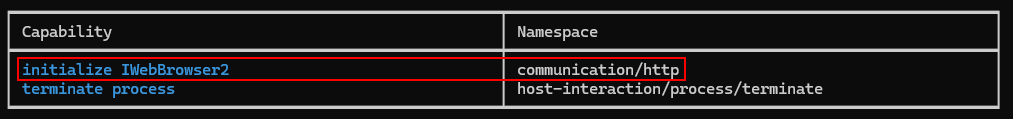
CAPA results tell us that this malware tries to access the internet by IWebBrowser2.
After we execute the malware, we see that it tries to access the URL that we found with Pestudio.
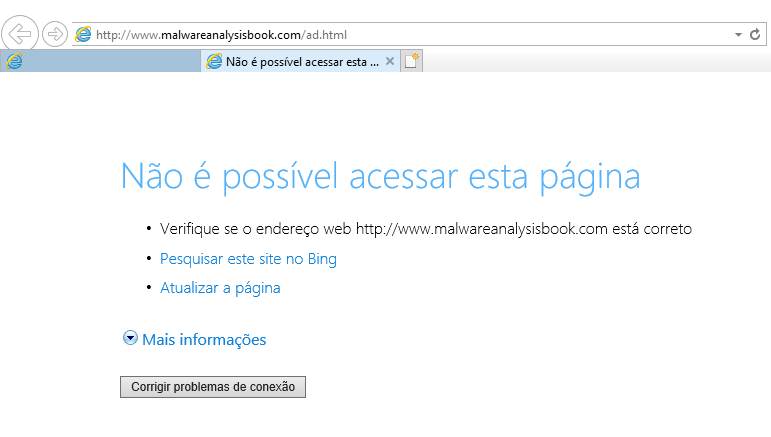
IE trying to access the malicious url
This is all its behavior, so we can stop here and let’s dive into the reversing process.
GNISREVER ←:
Open it up in IDA we can see a simple program contending some ifs statements, probably for some validations.
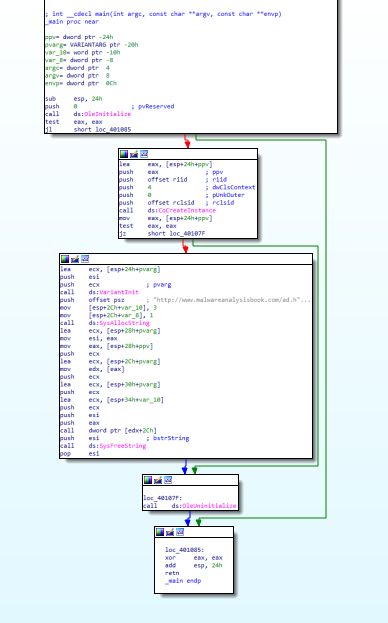
Main functions
As we already know, this program uses COM to request the URL. So, let’s insert the structures in IDA. Just go to the structures tab > Press the “INS” key > Add Standard Structure and select the IWebBrowser2Vtbl structure. Back to the disassembly view, we can now add the correct struct.
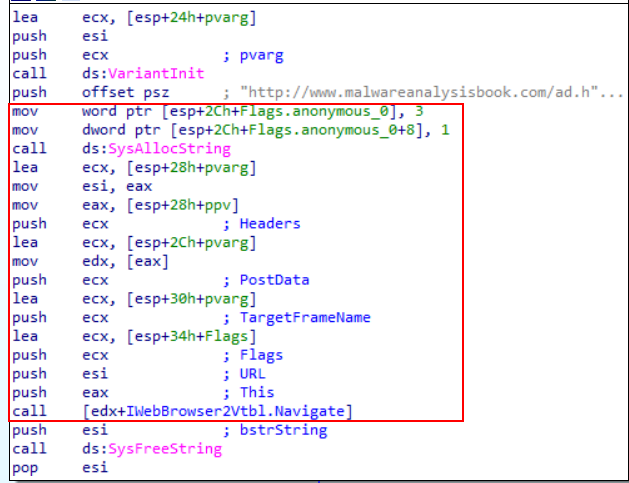
Right structures
With that, we can jump to the decompiler and retype some things!
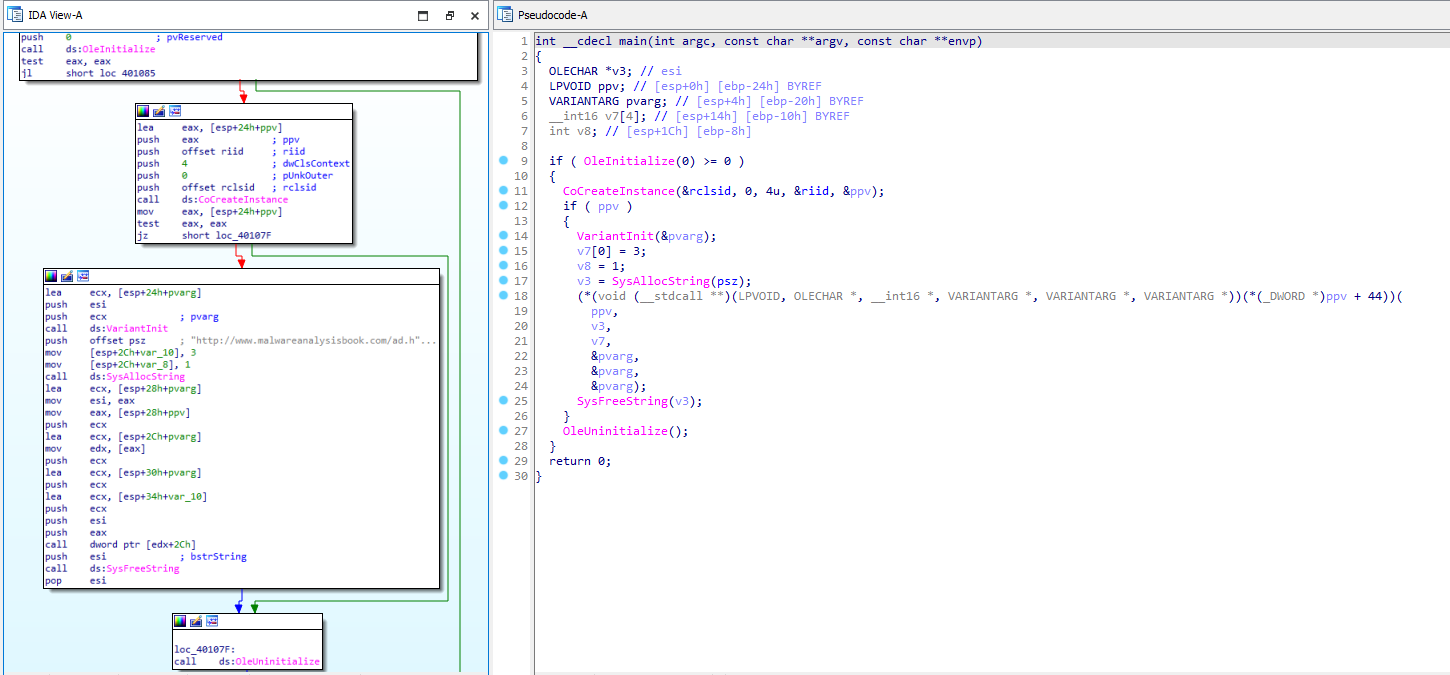
Before
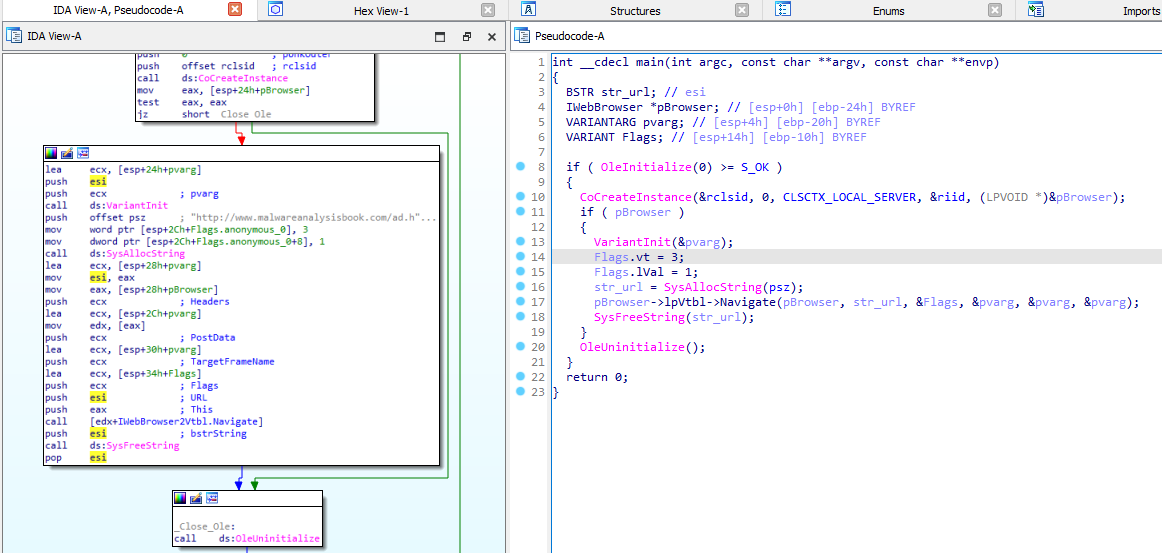
After
Our final code can be seen below:
#include <Windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <exdisp.h>
int main(void)
{
VARIANT pvarg = { 0 };
BSTR str_url;
IWebBrowser2* pBrowser = nullptr;
if (OleInitialize(NULL) >= S_OK)
{
// CLSID_InternetExplorer = 0002DF01-0000-0000-C000-000000000046
// IID_IWebBrowser2 = D30C1661-CDAF-11D0-8A3E-00C04FC9E26E
HRESULT hr = CoCreateInstance(CLSID_InternetExplorer, NULL, CLSCTX_LOCAL_SERVER, IID_IWebBrowser2, (void**)&pBrowser);
if (pBrowser)
{
VariantInit(&pvarg);
str_url = SysAllocString(L"http://192.0.0.128:8000/hello.html");
/* pvarg.vt & pvarg.lVal specifies that the navigation should open in a new window. */
pvarg.vt = 3;
pvarg.lVal = 1;
pBrowser->Navigate(str_url, &pvarg, &pvarg, &pvarg, &pvarg);
SysFreeString(str_url);
}
}
OleUninitialize();
return 0;
}
Conclusion:
As we can see, this simple downloader utilizes COM functions to perform an request to a malicious URL.




